Pronouns, typically the second topic covered in parts of speech, are words that substitute for nouns. In this article, you’ll delve into their definition, various types, and how they function within sentences. Pronouns play a pivotal role in language, facilitating smoother and more concise communication by replacing repetitive use of nouns.
What is pronoun?
A pronoun is a word that is used in place of a noun to avoid repetition and add variety to language. Pronouns are essential for clear and effective communication, as they help refer to individuals or objects without constantly repeating their names.

How are pronouns used in sentences?
The main function of pronouns is to replace nouns. Because of this, they are used in sentences in similar ways to nouns.
Like nouns, pronouns commonly serve as the subject of a sentence, followed by a verb (a word expressing an action).Examples:
Pronouns as subjects :
I like to play chess.
We have never been to Germany before.
It is difficult to stay calm in stressful situations.
A pronoun can also function as the object in a sentence—either a direct or indirect object:
- The direct object is something or someone that is directly acted upon by the verb.
- The indirect object is someone or something that receives the direct object.
Examples: Pronouns as direct and indirect objects:
Give me that!
Can you promise her this?
Types of pronoun:
Here are some common types of pronouns and their uses, along with examples:
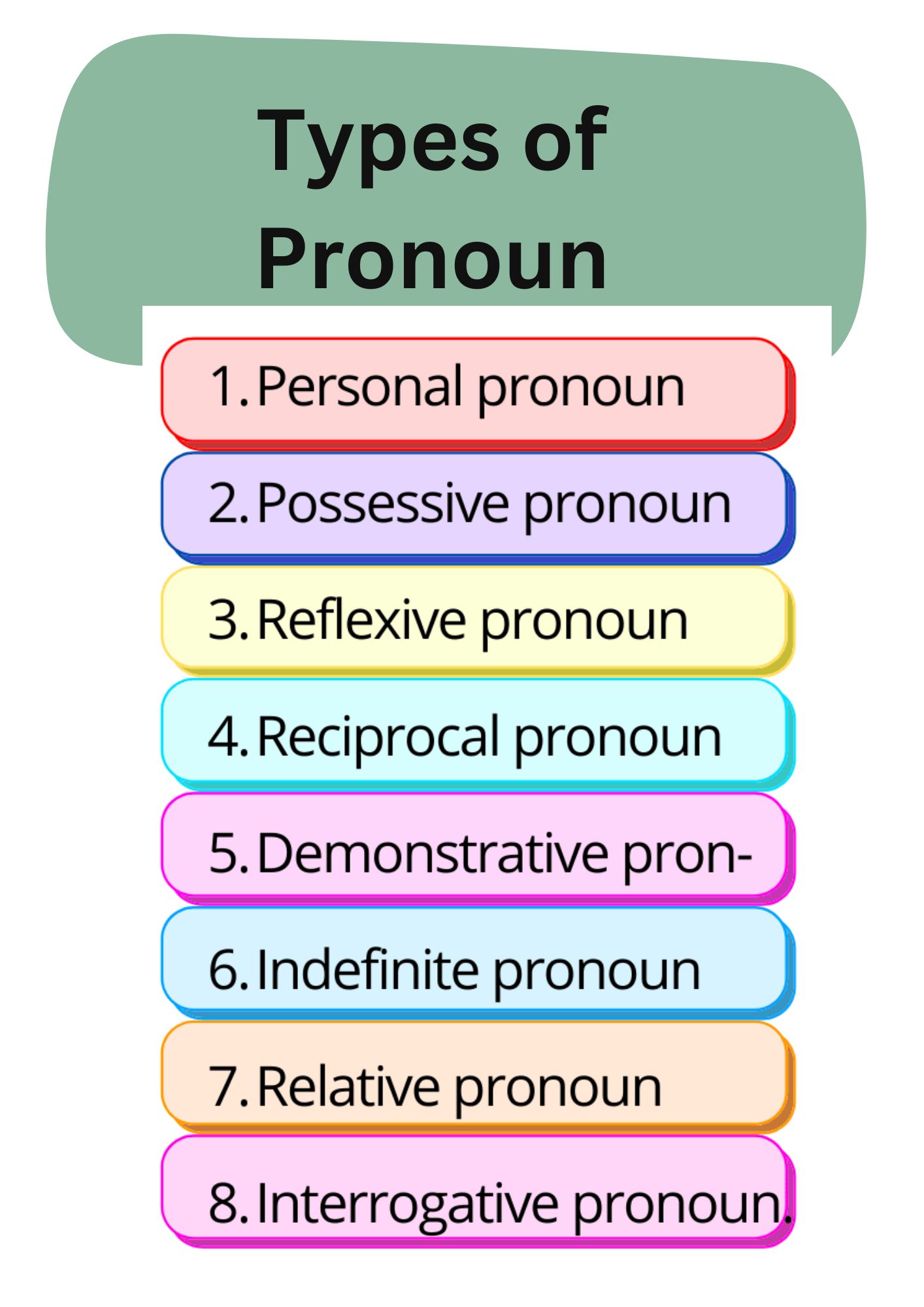
Personal Pronouns:
A personal pronoun is a type of pronoun that refers to a specific person or thing. Personal pronouns replace nouns in sentences to avoid repetition and make the language more concise. Personal pronouns can represent different grammatical persons, including the first person (the speaker), the second person (the person being spoken to), and the third person (the person or thing being spoken about).
| Personal pronoun | number | subject | object | possessive |
| 1st person | singular | I | me | my, mine |
| plural | We | us | our, ours | |
| 2nd person | singular | you | you | your, yours |
| plural | you | you | your, yours | |
| 3rd person | singular | He, she | Him, Her | His, Her, Hers |
| plural | They | Them | their, theirs |
Here are examples of personal pronouns used in sentences:
- First Person Singular:
- I went to the store.
- Can you pass me the salt?
- My name is John, and I like to read.
- First Person Plural:
- We are going to the movies tonight.
- Let’s finish our homework together.
- Our team won the championship.
- Second Person Singular:
- You should finish your dinner before dessert.
- Can you help me with this assignment?
- Are you coming to the party?
- Second Person Plural:
- You all need to be quiet during the exam.
- Did you enjoy the concert last night?
- Can you give me your opinions on this matter?
- Third Person Singular:
- He is going to the gym.
- She likes to play the piano.
- It is raining outside.
- Third Person Plural:
- They are going on vacation next week.
- The students are studying for their exams.
- The dogs barked loudly all night.
Possessive Pronouns:
A possessive pronoun is a type of pronoun that indicates ownership or possession. Possessive pronouns replace nouns and show who or what owns or possesses something.

Here are the possessive pronouns in English along with their uses and examples:
- My – indicates possession by the speaker.
- Example: This is my book.
- Your – indicates possession by the person being spoken to.
- Example: Is this your car?
- His – indicates possession by a male person or thing.
- Example: That is his house.
- Her – indicates possession by a female person or thing.
- Example: I saw her cat outside.
- Its – indicates possession by a non-human or non-gendered entity.
- Example: The dog wagged its tail.
- Our – indicates possession by a group including the speaker.
- Example: We all went to our favorite restaurant.
- Your – indicates possession by a group excluding the speaker.
- Example: Your tickets are on the table.
- Their – indicates possession by a group not including the speaker.
- Example: Their house is beautiful.
Demonstrative Pronouns:
Demonstrative pronouns are used to point to specific things or people. They indicate proximity in space or time and can replace nouns to avoid repetition.

Here are the demonstrative pronouns in English along with their uses and examples:
- This – indicates something that is nearby in space or time.
- Example: This is my favorite movie.
- That – indicates something that is further away in space or time.
- Example: I want that book on the shelf.
- These – indicates more than one thing that is nearby in space or time.
- Example: Can you pass me these pens?
- Those – indicates more than one thing that is further away in space or time.
- Example: I like those flowers in the garden.
Relative Pronouns:
A relative pronoun is a type of pronoun that introduces a relative clause and relates it to the noun it modifies. Relative clauses provide additional information about the noun in the main clause.

Here is a list of relative pronouns:
- Who: Refers to people.
- Example: The woman who lives next door is a doctor.
- Whom: Also refers to people, but often used in formal or more structured language. It is the object form of “who”.
- Example: The person whom I met yesterday is my new boss.
- Which: Refers to animals and things.
- Example: The book, which is on the table, is mine.
- That: Refers to people, animals, or things and can be used in restrictive clauses (essential information) in both formal and informal contexts.
- Example: The dog that barks loudly belongs to my neighbor.
- Whose: Indicates possession and can refer to people, animals, or things.
- Example: The boy whose bike was stolen is very upset.
- Where: Refers to a place or location.
- Example: This is the park where we used to play as children.
- When: Refers to a point in time.
- Example: I still remember the day when we first met.
- Why: Refers to reason or cause.
- Example: That’s the reason why I didn’t attend the party.
- Reflexive Pronouns:
- Reflect the action back on the subject.
- Examples: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves.
- Example: I cut myself while cooking.
Interrogative Pronouns:
An interrogative pronoun is a pronoun used to ask questions. They are used to inquire about people, things, or quantities. In English, there are primarily five interrogative pronouns: who, whom, whose, what, and which. Here’s a breakdown of each with their uses and examples:

- Who: Used to ask about people.
- Example: Who is coming to the party?
- Example: Who won the game?
- Whom: Also used to ask about people, but specifically about the object of a verb or preposition.
- Example: Whom did you invite to the party?
- Example: To whom did you give the book?
- Whose: Indicates possession or ownership.
- Example: Whose bag is this?
- Example: Whose car did you borrow?
- What: Used to inquire about things, actions, or ideas.
- Example: What is your favorite color?
- Example: What are you doing tonight?
- Which: Used to choose between a limited number of options.
- Example: Which book do you want to read?
- Example: Which route should we take?
Indefinite Pronouns:
An indefinite pronoun is a pronoun that is used to substitute nouns that are not specific. Indefinite pronouns can be used in the singular and plural forms. These are pronouns that do not refer to any specific person, thing, or amount. They are more general and often refer to an unspecified or unknown entity. There are several kinds of indefinite pronouns, including:
- Some: Used for an unspecified amount or number.
- Example: “Can I have some water?”
- Any: Used to refer to one or some of a thing or things, no matter how much or how many.
- Example: “Do you have any questions?”
- Many: Referring to a large number or amount.
- Example: “Many people attended the concert.”
- Few: Referring to a small number or amount.
- Example: “There are few apples left.”
- Several: Referring to an unspecified but relatively small number.
- Example: “Several students volunteered to help.”
- None: Referring to no amount or not any.
- Example: “There is none left.”
- All: Referring to the whole quantity or extent of something.
- Example: “All the cookies are gone.”
Reciprocal Pronouns:
A reciprocal pronoun is a pronoun that indicates a mutual action or relationship between two or more individuals. In English, the reciprocal pronoun is “each other” or “one another.” These pronouns are used when actions are being reciprocated between the subjects of the sentence. Here’s a breakdown of reciprocal pronouns with their uses and examples:
- Each Other: This reciprocal pronoun is used when referring to two individuals or groups reciprocating an action.
- Example: Sarah and Tom hugged each other.
- Example: The two teams congratulated each other after the game.
- One Another: This reciprocal pronoun is also used to indicate a mutual action or relationship, but it’s used when referring to more than two individuals or groups reciprocating an action.
- Example: The members of the committee respect one another’s opinions.
- Example: The children in the class help one another with their homework.
Reciprocal pronouns are used to express mutual interactions or relationships between the subjects involved. They are essential for indicating reciprocity in sentences.
Worksheets:
Worksheet 1: Identifying Personal Pronouns
Instructions: Circle the personal pronouns in each sentence.
- Maria went to the store to buy groceries.
- He likes to play soccer with his friends.
- She enjoys reading books before bedtime.
- They are going to the park to have a picnic.
- I am learning how to ride a bicycle.
Worksheet 2: Fill in the Blanks with Demonstrative Pronouns
Instructions: Fill in the blanks with the appropriate demonstrative pronoun (this, that, these, those).
- ___________ is my favorite toy.
- ___________ cookies are delicious!
- Can you pass me ___________ book?
- I want to buy ___________ new shoes.
- ___________ is the tallest building in the city.
Worksheet 3: Match the Interrogative Pronouns
Instructions: Match the interrogative pronouns with their corresponding questions.
- _____ is your name? A. Who
- _____ are you going with? B. What
- _____ do you like to do on weekends? C. Where
- _____ is your dog? D. When
- _____ did you go on vacation? E. Why
Worksheet 4: Identify the Indefinite Pronouns
Instructions: Underline the indefinite pronouns in each sentence.
- Some of the cake was eaten by the guests.
- None of the students finished their homework.
- Many people attended the concert last night.
- There is little milk left in the refrigerator.
- All the books on the shelf belong to me.
Worksheet 5: Reciprocal Pronouns Crossword Puzzle
Instructions: Complete the crossword puzzle with the correct reciprocal pronouns.
- Across
- Members of a group help _____ with their tasks. (6 letters)
- Sarah and Tom hugged _____ after not seeing each other for a long time. (9 letters)
- Down 2. The two teams congratulated _____ after the game. (9 letters)
- The children in the class respect _____ opinions. (4 letters)
Answer Key:
- Each Other
- One Another
- One Another
- Each Other
Conclusion
In conclusion, pronouns play a crucial role in language by replacing nouns to avoid repetition and enhance clarity and flow in communication. Through this exploration of various types of pronouns—personal, demonstrative, interrogative, indefinite, and reciprocal—it becomes evident that each serves a distinct function in expressing ideas and relationships within sentences. Understanding and mastering the use of pronouns not only improves writing and speaking skills but also fosters effective communication. As such, embracing the versatility and significance of pronouns enriches language comprehension and expression, empowering individuals to convey their thoughts and ideas with precision and efficiency.


Hi there! Just wanted to let you know how much I enjoyed reading this post. Your approach to the subject was unique and informative. It’s clear that you put a lot of effort into your writing. Keep up the great work, and I can’t wait to see what else you have in store.