Introduction:
Suffixes are essential components of word formation in language. They are a type of affix, a morpheme added to the end of a word, altering its meaning or grammatical function. Suffixes play a crucial role in expanding vocabulary, modifying word forms, and expressing grammatical features. Understanding suffixes is fundamental for grasping the intricacies of word formation and usage in any language.
What is a Suffix?
A suffix is a group of letters added to the end of a word to change its meaning or to form a new word. It’s like a small word piece that attaches to the end of another word to give it a different function or meaning.
Examples include:
- -ly: quickly, slowly
- -er: faster, taller
- -ness: happiness, darkness
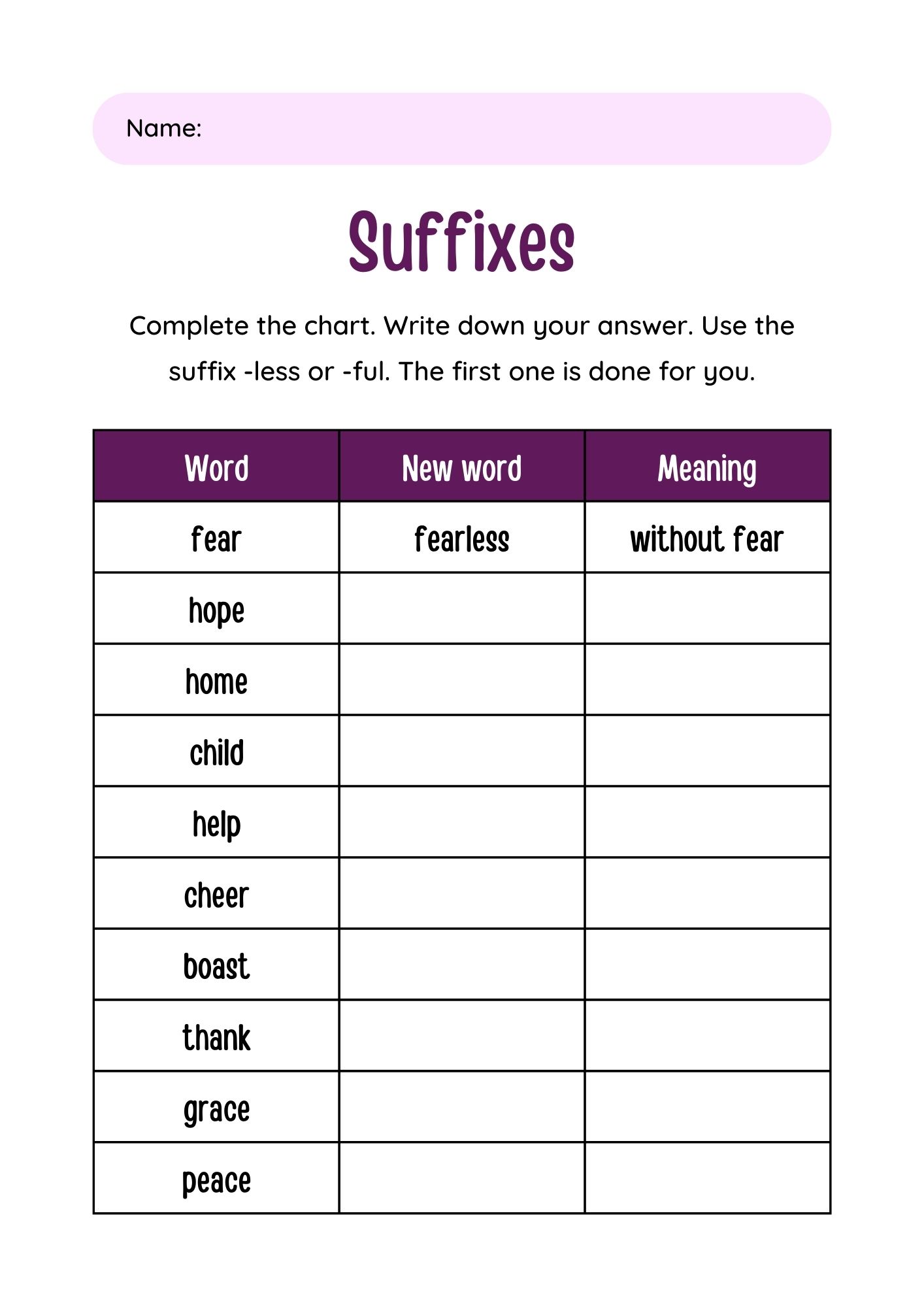
- -ful: helpful, beautiful
- -tion: action, creation
- -ment: movement, excitement
- -less: fearless, careless
- -able: lovable, enjoyable
- -ed: walked, jumped
- -ing: running, singing
These examples demonstrate how suffixes modify words to convey different meanings or functions.
Types of Suffixes:
- Derivational Suffixes
- Inflectional Suffixes
Derivational Suffixes:
Noun Suffixes:
A noun suffix is a group of letters added to the end of a word to form a noun or to modify its meaning. They can change the formation of various parts of speech, including verbs, adjectives, and even other nouns. Here are some common noun suffixes and how they change the formation of different parts of speech:
- –ment:
- Meaning: Denotes the result or product of an action.
- Examples:
- Verb -> Noun: Govern (verb) -> Government (noun)
- Verb -> Noun: Enforce (verb) -> Enforcement (noun)
- –tion / -sion:
- Meaning: Denotes an action or process.
- Examples:
- Verb -> Noun: Act (verb) -> Action (noun)
- Verb -> Noun: Confuse (verb) -> Confusion (noun)
- -ity / -ty:
- Meaning: Denotes a state, quality, or condition.
- Examples:
- Adjective -> Noun: Real (adjective) -> Reality (noun)
- Adjective -> Noun: Happy (adjective) -> Happiness (noun)
- -ness:
- Meaning: Denotes a state or quality.
- Examples:
- Adjective -> Noun: Kind (adjective) -> Kindness (noun)
- Adjective -> Noun: Dark (adjective) -> Darkness (noun)
- -er / -or:
- Meaning: Denotes a person or thing that performs an action or has a particular quality.
- Examples:
- Verb -> Noun: Teach (verb) -> Teacher (noun)
- Verb -> Noun: Act (verb) -> Actor (noun)
- -hood:
- Meaning: Denotes a state or condition of being.
- Examples:
- Noun -> Noun: Neighbor (noun) -> Neighborhood (noun)
- Noun -> Noun: Brother (noun) -> Brotherhood (noun)
- -ism:
- Meaning: Denotes a belief, doctrine, principle, or practice.
- Examples:
- Adjective -> Noun: Real (adjective) -> Realism (noun)
- Adjective -> Noun: Optimistic (adjective) -> Optimism (noun)
- -ance / -ence:
- Meaning: Denotes an action, process, or state.
- Examples:
- Verb -> Noun: Appear (verb) -> Appearance (noun)
- Verb -> Noun: Convince (verb) -> Convincence (noun)
- -ship:
- Meaning: Denotes a state, condition, or quality of being.
- Examples:
- Noun -> Noun: Friend (noun) -> Friendship (noun)
- Noun -> Noun: Leader (noun) -> Leadership (noun)
Adjective suffixes:
Adjective suffixes are affixes added to the end of a word to create adjectives, which are words that describe or modify nouns. These suffixes can typically be added to various parts of speech to form adjectives. Here are some common adjective suffixes and the parts of speech to which they can be added:
- -able / -ible:
- Meaning: Capable of or suitable for.
- Examples:
- Verb -> Adjective: Enjoy (verb) -> Enjoyable (adjective) – Capable of being enjoyed.
- Noun -> Adjective: Access (noun) -> Accessible (adjective) – Capable of being accessed.
- -al:
- Meaning: Pertaining to or characterized by.
- Examples:
- Noun -> Adjective: Nature (noun) -> Natural (adjective) – Pertaining to nature.
- Noun -> Adjective: Nation (noun) -> National (adjective) – Pertaining to a nation.
- -ent / -ant:
- Meaning: Showing or performing a specified action.
- Examples:
- Verb -> Adjective: Depend (verb) -> Dependent (adjective) – Showing dependence.
- Verb -> Adjective: Assist (verb) -> Assistant (adjective) – Performing assistance.
- -ful:
- Meaning: Full of; characterized by.
- Examples:
- Noun -> Adjective: Joy (noun) -> Joyful (adjective) – Full of joy.
- Noun -> Adjective: Help (noun) -> Helpful (adjective) – Characterized by help.
- -ic:
- Meaning: Relating to or characterized by.
- Examples:
- Noun -> Adjective: Music (noun) -> Musical (adjective) – Relating to music.
- Noun -> Adjective: Logic (noun) -> Logical (adjective) – Characterized by logic.
- -ish:
- Meaning: Having the qualities of; somewhat.
- Examples:
- Noun -> Adjective: Child (noun) -> Childish (adjective) – Having the qualities of a child.
- Noun -> Adjective: Fool (noun) -> Foolish (adjective) – Somewhat foolish.
- -ive:
- Meaning: Tending to; inclined to.
- Examples:
- Noun -> Adjective: Talk (noun) -> Talkative (adjective) – Inclined to talk.
- Noun -> Adjective: Attract (noun) -> Attractive (adjective) – Tending to attract.
- -ous:
- Meaning: Possessing, full of, or characterized by.
- Examples:
- Noun -> Adjective: Courage (noun) -> Courageous (adjective) – Possessing courage.
- Noun -> Adjective: Adventure (noun) -> Adventurous (adjective) – Full of adventure.
- -y:
- Meaning: Characterized by; inclined to.
- Examples:
- Noun -> Adjective: Sun (noun) -> Sunny (adjective) – Characterized by sun.
- Noun -> Adjective: Mess (noun) -> Messy (adjective) – Inclined to mess.
Adverb suffixes:
Adverb suffixes are affixes added to words, typically adjectives or nouns, to form adverbs, which modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Here’s a breakdown of some common adverb suffixes along with their meanings and examples:
-ly:
- This suffix is one of the most common adverb suffixes. When added to adjectives, it transforms them into adverbs, indicating manner or quality.
- Meaning: Indicates manner or quality.
- Examples:
- calmly (manner: in a calm manner)
- easily (manner: with ease)
- quickly (manner: in a quick manner)
-ward(s):
- This suffix denotes direction or orientation.
- Meaning: Indicates direction or orientation.
- Examples:
- downwards (direction: toward a lower place)
- homeward(s) (direction: toward home)
- upwards (direction: toward a higher place)
3.-wise:
It indicates the manner or direction in which something is done.
- Meaning: Indicates the manner or direction.
- Examples:
- anti-clockwise (direction: in the opposite direction to the movement of the hands of a clock)
- clockwise (direction: in the same direction as the movement of the hands of a clock)
- edgewise (manner: in a sideways direction, as if moving through a narrow space)
Verb suffixes:
Verb suffixes are affixes added to verbs to modify their meaning or indicate tense, aspect, mood, voice, or other grammatical features. Here’s a list of common verb suffixes along with examples:
1.ate (Infinitive):
Forms infinitive verbs, indicating the base or uninflected form of a verb.
- Example: create (to create), illuminate (to illuminate), participate (to participate)
2.-ize, -ise (Verb Forming):
Forms verbs from nouns or adjectives, often indicating the process or action of the base word.
- Example: organize (to organize), realize (to realize), advertise (to advertise)
3.-ify (Verb Forming):
Forms verbs from nouns or adjectives, typically implying the action of making or causing something.
- Example: simplify (to simplify), amplify (to amplify), beautify (to beautify)
-en (Causative):
Forms causative verbs, indicating the action of making something longer, higher, wider, etc.
- Example: lengthen (to lengthen), heighten (to heighten), widen (to widen)
-fy (Verb Forming):
Forms verbs from nouns or adjectives, often suggesting the action of making or rendering in a certain way.
- Example: clarify (to clarify), terrify (to terrify), glorify (to glorify)
Inflectional suffixes:
Inflectional suffixes are affixes added to words to indicate grammatical features such as tense, number, aspect, mood, person, or case. Unlike derivational suffixes, they do not change the basic meaning or part of speech of the base word. Instead, they modify the word to convey grammatical information. Here are the types of inflectional suffixes along with examples:
- Plural Suffix (-s, -es):
- -s: Adds plurality to countable nouns in the singular form.
- Example: cat → cats
- -es: Used for pluralization when the base word ends in -s, -x, -z, -ch, -sh, or consonant + y.
- Example: box → boxes
- -s: Adds plurality to countable nouns in the singular form.
- Possessive Suffix (-‘s, -s’):
- -‘s: Indicates possession or ownership.
- Example: dog → dog’s
- -s’: Used for possessive forms of plural nouns ending in -s.
- Example: dogs → dogs’
- -‘s: Indicates possession or ownership.
- Third Person Singular Present Tense (-s):
- -s: Marks the third person singular present tense of verbs.
- Example: walk → walks
- -s: Marks the third person singular present tense of verbs.
- Past Tense Suffix (-ed):
- -ed: Indicates past tense for regular verbs.
- Example: talk → talked
- -ed: Indicates past tense for regular verbs.
- Past Participle Suffix (-en, -ed):
- -en: Forms past participles for irregular verbs.
- Example: break → broken
- -ed: Forms past participles for regular verbs.
- Example: play → played
- -en: Forms past participles for irregular verbs.
- Comparative and Superlative Suffixes (-er, -est):
- -er: Forms the comparative degree of adjectives.
- Example: tall → taller
- -est: Forms the superlative degree of adjectives.
- Example: tall → tallest
- -er: Forms the comparative degree of adjectives.
Rules of adding suffixes:
When you’re adding a suffix to a word, just remember these simple rules:
For most words: Just add the suffix without changing the original word. For example, “happy” becomes “happily” by adding “-ly.”
Words ending in ‘y’: If a word ends in ‘y’ and it has a consonant before it, change the ‘y’ to ‘i’ before adding a suffix. For example, “carry” becomes “carrying” by changing ‘y’ to ‘i’ before adding “-ing.”
Irregular words: Some words don’t follow these rules and need to be memorized individually. For example, “go” becomes “went” instead of “goed” in the past tense.\

Conclusion:
In the world of language, suffixes are like the building blocks that help us create and understand words. They add meaning and change the function of words, making communication clearer and more interesting. Just as people grow and change over time, words can transform with the addition of suffixes. Suffixes help us express ourselves better and connect with others through the shared language we use every day. They’re like the small but important pieces that complete the puzzle of language, making it rich, diverse, and endlessly fascinating.