English grammar is full of shades, especially when referring to past actions. There are four main past tenses in English; each serves a certain purpose and sometimes looks or is similar in meaning to another tense. This guide will explore the Past Simple, Past Continuous, Past Perfect, and Past Perfect Continuous while showing how they compare with other tenses. By mastering these tenses, you will denote past events more precisely.
Past tense:
The past tense is a verb tense that defines an action or event that took place at one point in the past. The usage indicates that something was completed prior to the present time.
There are four main types of past tense in English:

1. Past Simple:
The simple past tense is used to describe actions, events, or states that were completed at a specific time in the past. It is one of the most common tenses in English, used for a wide range of situations when talking about the past.
- Example: She danced at the party yesterday.
Key Point: The action is finished, and the specific time is clear.

Examples of Past Simple Usage in a Table:
| Sentence Type | Example Sentence | Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | She visited Paris last year. | Subject + Verb (past) + Object |
| Negative | She did not visit Paris. | Subject + did not + Base form of verb + Object |
| Question | Did she visit Paris? | Did + Subject + Base form of verb + Object |
Usage of Simple Past Tense
- Completed Actions in the Past
- The simple past is used to describe actions that started and ended at a specific point in the past.
- Example: “I finished my homework last night.”
- Actions that Happened One After Another in the Past
- When narrating events or describing actions that occurred sequentially.
- Example: “She entered the room, sat down, and opened her book.”
- Repeated or Habitual Actions in the Past
- Describes actions or events that occurred regularly or repeatedly in the past but are no longer happening.
- Example: “When I was a child, I played soccer every weekend.”
- States in the Past
- Describes states of being or conditions that were true in the past but no longer apply.
- Example: “He was a teacher before he became a writer.
Time Expressions for Specific Points in the Past:
Here’s a table with common time expressions used in the past simple tense to indicate specific points in the past:
| Time Expression | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Yesterday | I finished the report yesterday. |
| Last night | She watched a movie last night. |
| Last week | They traveled to New York last week. |
| Last month | He joined the company last month. |
| Last year | We went to Spain last year. |
| An hour ago | She called me an hour ago. |
| A few minutes ago | I received the email a few minutes ago. |
| In 1990 | They moved to Canada in 1990. |
| On my birthday | He gave me a gift on my birthday. |
| When I was young | We lived in a small village when I was young. |
| The other day | I saw him the other day at the mall. |
| Three days ago | She returned from vacation three days ago. |
| At 9:00 a.m. | The meeting started at 9:00 a.m. |
- Yesterday
- Example: “I saw her yesterday.”
- Last night
- Example: “We had dinner last night.”
- Last week/month/year
- Example: “She moved to London last year.”
- Ago
- Example: “They arrived two hours ago.”
- In + year
- Example: “He was born in 1990.”
- On + day/date
- Example: “I went to the concert on Monday.”
- Example: “She left the office on June 1st.”
Expressions for General Periods in the Past:
- The day before yesterday
- Example: “I called her the day before yesterday.”
- The other day
- Example: “I met him the other day.”
- Once
- Example: “She traveled to Paris once.”
- In the past
- Example: “People used to write letters in the past.”
- When I was a child/teenager
- Example: “I played soccer every weekend when I was a child.”
Expressions for Habitual Actions in the Past:
- Every day/week/month/year
- Example: “We went to the beach every summer.”
- Often
- Example: “She often visited her grandparents.”
- Always
- Example: “He always walked to school.”
- Frequently
- Example: “They frequently traveled to New York for business.”
- Never
- Example: “He never liked vegetables.”
Expressions Indicating Specific Durations in the Past:
- For + period of time
- Example: “She lived in Japan for three years.”
- From … to …
- Example: “They worked there from 2005 to 2010.”
- All day/night/week/month
- Example: “I studied all night for the exam.”
Comparison with Present Perfect:
- The Past Simple focuses on when something happened, while the Present Perfect (e.g., I have danced) focuses on the result or relevance to the present.
- Past Simple: I went to the store yesterday (specific time).
- Present Perfect: I have gone to the store (relevant to now; time unspecified).
Key Differences Between Simple Past and Present Perfect
| Aspect | Simple Past | Present Perfect |
|---|---|---|
| Time Reference | Refers to a specific time in the past (often mentioned) | Refers to an unspecified time in the past (no exact time) |
| Focus | Focuses on when the action happened | Focuses on the result or experience (present relevance) |
| Action Status | Action is fully completed in the past | The action may have present consequences or be ongoing |
| Time Expressions | Uses expressions like: yesterday, last week, in 1999 | Uses expressions like: just, already, ever, never, since, for |
| Examples | “I saw him yesterday.” | “I have seen him recently.” |
| Usage with Duration | Describes past actions completed at a specific time | Describes actions continuing from the past to the present |
| Questions | “Did you see the movie?” | “Have you seen the movie?” |
Simple Past: “I finished the report yesterday.”
The action of finishing the report was completed at a specific time in the past (yesterday).
Present Perfect: “I have finished the report.”
The action of finishing the report is important now; the exact time isn’t specified, but the fact that it’s done is relevant to the present.
Usage Situations:
Talking about experiences:
Simple Past: “I visited Italy in 2018.” (specific time)
Present Perfect: “I have visited Italy.” (no time specified, focus on experience)
Ongoing situations:
Simple Past: “She worked here for five years.” (She no longer works here.)
Present Perfect: “She has worked here for five years.” (She still works here.)
With “just, already, yet”:
Simple Past: “I didn’t finish the project yet.” (Incorrect use)
Present Perfect: “I haven’t finished the project yet.” (Correct)
Resembles:
- Present Simple: The Present Simple talks about habits and routines in the present, but in Past Simple, these routines or facts were true in the past.
- She works at a bank (Present Simple).
- She worked at a bank (Past Simple).
The past simple and present simple tenses have similarities in structure and usage, though they refer to different timeframes. Here’s a comparison of the two in a table:
| Aspect | Past Simple | Present Simple |
|---|---|---|
| Time Reference | Refers to completed actions in the past. | Refers to habitual actions, facts, or general truths in the present. |
| Affirmative Structure | Subject + Verb (past form) | Subject + Verb (base form; adds -s for he/she/it) |
| Negative Structure | Subject + did not + Verb (base form) | Subject + do/does not + Verb (base form) |
| Question Structure | Did + Subject + Verb (base form)? | Do/Does + Subject + Verb (base form)? |
| Common Uses | – Completed actions – Past habits – Past facts | – Habits – General truths – Scheduled events |
| Examples (Affirmative) | “She visited the museum yesterday.” | “She visits the museum every month.” |
| Examples (Negative) | “They did not finish the project on time.” | “They do not finish projects early.” |
| Examples (Question) | “Did he study last night?” | “Does he study every night?” |
2. Past Continuous:
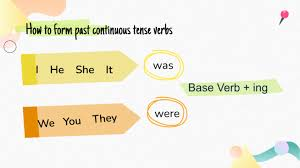
The past continuous tense (also called the past progressive tense) is used to describe actions or events that were ongoing or in progress at a specific time in the past. It is formed using the past tense of the verb “to be” (was or were) followed by the present participle (base verb + -ing).
Form: Subject + was/were + verb (-ing)
- Example: They were watching TV when the phone rang.
Past Continuous Usage and Rules:
| Usage | Rule | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Ongoing action in the past | Subject + was/were + Verb(-ing) | She was reading a book. |
| Interrupted action | Past continuous for the ongoing action; past simple for the action that interrupted it. | They were having dinner when the phone rang. |
| Setting the scene | Use past continuous to describe background activities or settings. | It was raining, and people were hurrying home. |
| Two simultaneous actions | Subject + was/were + Verb(-ing) + while + Subject + was/were + Verb(-ing) | I was cooking while he was setting the table. |
| Repeated past actions | Used to show repeated or habitual actions in the past (often with “always”). | He was always talking loudly during meetings. |
Structure
| Sentence Type | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Subject + was/were + Verb(-ing) | They were studying for their exams. |
| Negative | Subject + was/were + not + Verb(-ing) | I was not feeling well yesterday. |
| Question | Was/Were + Subject + Verb(-ing)? | Were you listening to the teacher? |
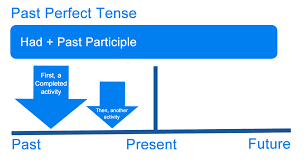
3. Past Perfect:
The past perfect tense describes an action that was completed before another action or point in time in the past. It is formed using the auxiliary verb “had” followed by the past participle of the main verb.
Form: Subject + had + past participle
- Example: By the time I arrived, she had left.
Usage:
- Describes an action that was completed before another action or point in the past.
- Often used to show sequence of events, where one action happened earlier.
Rules:
- Earlier Action in the Past: The past perfect is used to indicate the action that happened first when two actions occurred in the past.
- Example: I had finished my homework before the movie started.
- Specific Time or Event in the Past: It is used to show that an action was completed before a specific time or event in the past.
- Example: She had already left when I arrived.
- Reported Speech: The past perfect is used in reported speech to express an action that was completed before the reporting time.
- Example: He said that he had visited Paris the previous year.
- Conditional Sentences: It is used in third conditional sentences to express hypothetical situations.
- Example: If I had studied harder, I would have passed the exam.
Examples:
- By the time we got to the station, the train had already departed.
- He had never seen snow until he moved to Canada.
- They had cleaned the house before the guests arrived.
- She had forgotten her keys, so she couldn’t unlock the door.
Comparison with Past Simple:
- The Past Perfect describes an action before another past event, while the Past Simple describes events in order.
- Past Perfect: She had left before I arrived (the leaving happened first).
- Past Simple: She left when I arrived (both actions are presented in sequence).
Resembles:
- Present Perfect: Both tenses describe an action that is relevant to another point, but Present Perfect links an action to the present, whereas Past Perfect links it to the past.
- Past Perfect: I had already eaten when they arrived (before another past event).
- Present Perfect: I have already eaten (relevant now).
4. Past Perfect Continuous:
The past perfect continuous tense is used to describe an action that started in the past, continued for some time, and was still ongoing or had recently stopped before another action or point in the past. It emphasizes the duration of the action.
Form: Subject + had been + verb (-ing)
- Example: She had been working for three hours before the meeting started.

Usage:
- Describes an action that was ongoing for some time before another action or point in the past.
- Used to emphasize the duration of an action before something else happened.
Rules of Past Perfect Continuous Tense:
- Action Ongoing Before Another Action:
- Use the past perfect continuous to describe an action that started and continued for some time before another action in the past.
- Example: She had been studying for hours when the power went out.
- Emphasis on Duration:
- It is often used with time expressions such as for and since to emphasize the length of time the action had been happening.
- Example: They had been waiting for the bus for 30 minutes before it arrived.
- Cause and Effect:
- It can explain the cause of something in the past, often implying that the action was ongoing and led to a result.
- Example: He was tired because he had been working all day.
- Interrupted Action:
- Use it when one ongoing action was interrupted by another action in the past.
- Example: We had been walking for hours when it suddenly started raining.
Examples:
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| I had been reading the book for two hours. | Focuses on the duration of the reading before a specific moment in the past. |
| They had been playing football before dinner. | The activity of playing was ongoing before the dinner event. |
| She had been working at the company for years before she quit. | Emphasizes the duration of her work before she left. |
Comparison with Past Continuous:
- The Past Perfect Continuous emphasizes the duration of an action before a point in the past, while Past Continuous focuses on the progress of an action at a specific time.
- Past Perfect Continuous: I had been studying for hours before the exam.
- Past Continuous: I was studying when you called.
Resembles:
- Present Perfect Continuous: Both tenses emphasize the ongoing nature of an action, but Present Perfect Continuous links the action to the present, while Past Perfect Continuous links it to another point in the past.
- Past Perfect Continuous: He had been running for an hour before it started raining.
- Present Perfect Continuous: He has been running for an hour (and is still running or the result is relevant now).
Key Differences and Resemblances Summary:
- Past Simple vs. Present Perfect: Focuses on when vs. relevance to the present.
- Past Continuous vs. Past Perfect Continuous: Ongoing action at a specific past time vs. ongoing action before another past event.
- Past Perfect vs. Past Simple: Action before another past action vs. events in sequence.
Worksheet:
1: Fill in the blanks with the correct tense
Instructions: Complete the sentences using the correct form of the verb in brackets.
- Past Simple: She _______ (visit) her grandmother last weekend.
- Past Continuous: While I _______ (read), my brother was playing video games.
- Past Perfect: By the time they arrived, the movie _______ (start).
- Past Perfect Continuous: He _______ (work) at the company for two years before he resigned.
- Mixed: They _______ (study) hard before the exam began.
Answers:
- visited
- was reading
- had started
- had been working
- had been studying
2: Rewrite the sentences in the specified tense
Instructions: Rewrite each sentence in the tense given in brackets.
- She reads a book. (Past Simple)
- They are playing football. (Past Continuous)
- I finish my homework. (Past Perfect)
- He waits for the bus. (Past Perfect Continuous)
- She sings beautifully. (Past Continuous)
Answers:
- She read a book.
- They were playing football.
- I had finished my homework.
- He had been waiting for the bus.
- She was singing beautifully.
3: Identify the tense
Instructions: Read the sentences and identify the tense (Past Simple, Past Continuous, Past Perfect, or Past Perfect Continuous).
- They had been planning the trip for weeks.
- I went to the market yesterday.
- She was watching TV when I called.
- He had already left when we arrived.
- I was eating lunch at 1 PM.
Answers:
- Past Perfect Continuous
- Past Simple
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect
- Past Continuous
4: Error correction
Instructions: Each sentence has an error in tense. Correct it.
- I was sleep when the alarm rang.
- They had ate lunch before the meeting started.
- He was reading when suddenly he hear a loud noise.
- We had been waited for an hour before the bus arrived.
- She finish her homework before going out.
Answers:
- I was sleeping when the alarm rang.
- They had eaten lunch before the meeting started.
- He was reading when suddenly he heard a loud noise.
- We had been waiting for an hour before the bus arrived.
- She had finished her homework before going out.
5: Mixed tense practice
Instructions: Choose the correct form of the verb in brackets to complete the sentence.
- By the time we got to the station, the train _______ (leave).
- She _______ (write) a letter when I entered the room.
- I _______ (see) that movie last week.
- They _______ (play) in the park for hours before it started to rain.
- He _______ (talk) to his friend when the teacher walked in.
Answers:
- had left
- was writing
- saw
- had been playing
- was talking
Conclusion
By understanding the differences between these four past tenses, you can express past actions with much greater precision and clarity. Each tense allows for nuanced communication, helping you indicate not only when something happened, but also whether it was ongoing, completed, or relevant to another event. Keep practicing these forms, and you’ll find them becoming second nature as you describe the past!