Prepositions are words that shows the relationships between a noun or pronoun and other elements in a sentence, indicating various types of connections such as direction, location, time, or manner. Prepositions are essential for constructing meaningful sentences, as they help to clarify how different parts of a sentence are related to each other.
Functions of Prepositions:
- Connecting Elements: Prepositions connect nouns/pronouns to other words, clarifying relationships.
- “The key is in the drawer.” (Connects “key” and “drawer”)
- Forming Prepositional Phrases: Prepositions often form prepositional phrases that function as adjectives or adverbs.
- Adjective Phrase: “The book on the table is mine.” (Describes “book”)
- Adverbial Phrase: “He ran across the street.” (Describes “ran”)
- Expressing Relationships: They express various relationships, including spatial, temporal, and logical relationships.
- “She waited for him.” (Logical relationship)
Position of Prepositions:
1.Before a Noun or Pronoun:
- Example: The book is on the table. (“on” shows the relationship between “the table” and “The book”).
2. In Prepositional Phrases:
- A prepositional phrase includes the preposition, its object (a noun or pronoun), and any modifiers of the object.
- Example: She walked through the park. (“through the park” is the prepositional phrase)
3. In Questions:
- In questions, prepositions often come at the end of the sentence.
- Example: What are you looking at? (“at” comes at the end)
4. In Infinitive Phrases:
- Sometimes, prepositions appear before infinitive phrases.
- Example: She had no choice but to leave. (“but” before “to leave”)
5. Idiomatic Expressions:
- Certain idiomatic expressions have fixed preposition placements.
- Example: He is good at playing chess. (“at” follows “good”)
6. In Relative Clauses:
- Prepositions can be placed at the beginning or end of relative clauses.
- Example: The house in which I grew up is old. (“in” at the beginning) / The house which I grew up in is old. (“in” at the end).
Types of preposition:
Prepositions may be arranged in the following classes:
- simple Prepositions
- Double prepositions
- compound prepositions
Simple Prepositions:
Simple prepositions are single-word prepositions that show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other parts of the sentence. They are straightforward and often denote basic relationships involving time, place, direction, manner, and other common aspects.
Common Simple Prepositions and Their Uses:
Prepositions of Time:

Prepositions of time help to indicate when something happens. Here is a list of common prepositions of time along with their uses and examples:
- At
- Use: Specific times, festivals, or certain expressions.
- Examples:
- We will meet at 6 PM.
- She left at midnight.
- The event starts at noon.
- He was born at Christmas.
On- Use: Days and dates.
- Examples:
- The meeting is on Monday.
- She was born on July 20th.
- They go to the gym on weekends.
- We have a party on New Year’s Eve.
- In
- Use: Months, years, centuries, long periods.
- Examples:
- He was born in August.
- The project started in 2020.
- They lived there in the 19th century.
- The flowers bloom in spring.
- By
- Use: Not later than a specific time.
- Examples:
- Please finish the report by Friday.
- She promised to be back by 5 PM.
- The package will arrive by tomorrow.
- He needs to submit his application by next week.
- Before
- Use: Earlier than a specific time.
- Examples:
- She left before noon.
- We must complete the task before the deadline.
- He arrived before me.
- Finish your homework before dinner.
- After
- Use: Later than a specific time.
- Examples:
- Let’s meet after lunch.
- She went to the gym after work.
- We will start after the meeting.
- He called me after the show.
- During
- Use: Throughout the course of a period.
- Examples:
- She was very quiet during the movie.
- We traveled during the holidays.
- He stayed awake during the night.
- They met during the conference.
- Until/Till
- Use: Up to a specific time.
- Examples:
- The store is open until 9 PM.
- We waited till the end.
- She worked until she finished.
- The show runs till next week.
- From…to
- Use: Indicates the beginning and end of a period.
- Examples:
- The class runs from 9 AM to 11 AM.
- They lived in Paris from 2010 to 2015.
- The exhibition is open from Monday to Friday.
- We are on vacation from June to August.
- For
- Use: Duration of time.
- Examples:
- He stayed there for a week.
- They have been friends for years.
- She will be in the city for a few days.
- I have known him for a long time.
- Since
- Use: Starting point in time, continuing to the present.
- Examples:
- She has been studying since morning.
- They have lived here since 2005.
- He has been waiting since 10 AM.
- We’ve been friends since childhood.
- Within
- Use: Inside a time period.
- Examples:
- The project must be completed within a week.
- She will return within an hour.
- He replied within minutes.
- The task should be done within the deadline.
| Preposition | Use | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| At | Specific times, festivals | At 6 PM, At midnight, At noon, At Christmas |
| On | Days and dates | On Monday, On July 20th, On weekends, On New Year’s Eve |
| In | Months, years, centuries, long periods | In August, In 2020, In the 19th century, In spring |
| By | Not later than a specific time | By Friday, By 5 PM, By tomorrow, By next week |
| Before | Earlier than a specific time | Before noon, Before the deadline, Before me, Before dinner |
| After | Later than a specific time | After lunch, After work, After the meeting, After the show |
| During | Throughout a period | During the movie, During the holidays, During the night, During the conference |
| Until/Till | Up to a specific time | Until 9 PM, Till the end, Until she finished, Till next week |
| From…to | Beginning and end of a period | From 9 AM to 11 AM, From 2010 to 2015, From Monday to Friday, From June to August |
| For | Duration of time | For a week, For years, For a few days, For a long time |
| Since | Starting point, continuing to present | Since morning, Since 2005, Since 10 AM, Since childhood |
| Within | Inside a time period | Within a week, Within an hour, Within minutes, Within the deadline |
Preposition of Place:1

Prepositions of place are used to describe the location or position of something. Here is a list of common prepositions of place along with their uses and examples:
- In
- Use: Inside an enclosed space or area.
- Examples:
- The keys are in the drawer.
- She lives in New York.
- There is a fly in the room.
- He is in the car.
- On
- Use: On a surface.
- Examples:
- The book is on the table.
- She left her phone on the bed.
- There is a picture on the wall.
- The cat is sleeping on the sofa.
- At
- Use: Specific points or places.
- Examples:
- She is waiting at the bus stop.
- We met at the entrance.
- He is at home.
- The concert is at the park.
- By/Beside
- Use: Next to; at the side of.
- Examples:
- The lamp is by the bed.
- The dog is sitting beside its owner.
- There is a house by the river.
- She sat beside him during the movie.
- Under
- Use: Beneath or below.
- Examples:
- The cat is under the table.
- The shoes are under the bed.
- He hid under the blanket.
- The ball rolled under the couch.
- Over
- Use: Above or higher than.
- Examples:
- The picture is over the fireplace.
- There is a bridge over the river.
- She held the umbrella over her head.
- The helicopter flew over the city.
- Above
- Use: Higher than or overhead.
- Examples:
- The clock is above the door.
- There are clouds above the mountains.
- The shelf is above the desk.
- The light is above the mirror.
- Below
- Use: Lower than.
- Examples:
- The temperature is below freezing.
- The submarine is below the surface of the water.
- The painting is hung below the shelf.
- The town is below sea level.
- Between
- Use: In the space separating two points.
- Examples:
- The park is between the library and the museum.
- She sat between her two friends.
- There is a path between the trees.
- The letter is between the pages of the book.
- Among
- Use: In the midst of multiple items or people.
- Examples:
- She found her ring among the leaves.
- The house is hidden among the trees.
- He was among the crowd.
- The treasure is buried among the ruins.
- Near
- Use: Close to.
- Examples:
- There is a school near my house.
- He lives near the station.
- The restaurant is near the park.
- They sat near the front.
- Next to
- Use: Beside or immediately adjacent to.
- Examples:
- She sat next to her friend.
- The pharmacy is next to the grocery store.
- He parked his car next to mine.
- The lamp is next to the couch.
- In front of
- Use: Before or ahead of.
- Examples:
- The car is parked in front of the house.
- She stood in front of the mirror.
- There is a statue in front of the building.
- He is in front of the class.
- Behind
- Use: At the back of.
- Examples:
- The garage is behind the house.
- He hid behind the tree.
- The dog is sleeping behind the sofa.
- The store is behind the mall.
- Opposite
- Use: Facing or across from.
- Examples:
- The restaurant is opposite the bank.
- She lives opposite the park.
- The school is opposite the library.
- He sat opposite me during the meet.
| Preposition | Use | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| In | Inside an enclosed space or area | In the drawer, In New York, In the room, In the car |
| On | On a surface | On the table, On the bed, On the wall, On the sofa |
| At | Specific points or places | At the bus stop, At the entrance, At home, At the park |
| By/Beside | Next to; at the side of | By the bed, Beside its owner, By the river, Beside him |
| Under | Beneath or below | Under the table, Under the bed, Under the blanket, Under the couch |
| Over | Above or higher than | Over the fireplace, Over the river, Over her head, Over the city |
| Above | Higher than or overhead | Above the door, Above the mountains, Above the desk, Above the mirror |
| Below | Lower than | Below freezing, Below the surface, Below the shelf, Below sea level |
| Between | In the space separating two points | Between the library and the museum, Between her friends, Between the trees, Between the pages |
| Among | In the midst of multiple items or people | Among the leaves, Among the trees, Among the crowd, Among the ruins |
| Near | Close to | Near my house, Near the station, Near the park, Near the front |
| Next to | Beside or immediately adjacent to | Next to her friend, Next to the grocery store, Next to mine, Next to the couch |
| In front of | Before or ahead of | In front of the house, In front of the mirror, In front of the building, In front of the class |
| Behind | At the back of | Behind the house, Behind the tree, Behind the sofa, Behind the mall |
| Opposite | Facing or across from | Opposite the bank, Opposite the park, Opposite the library, Opposite me |
Prepositions of Direction:
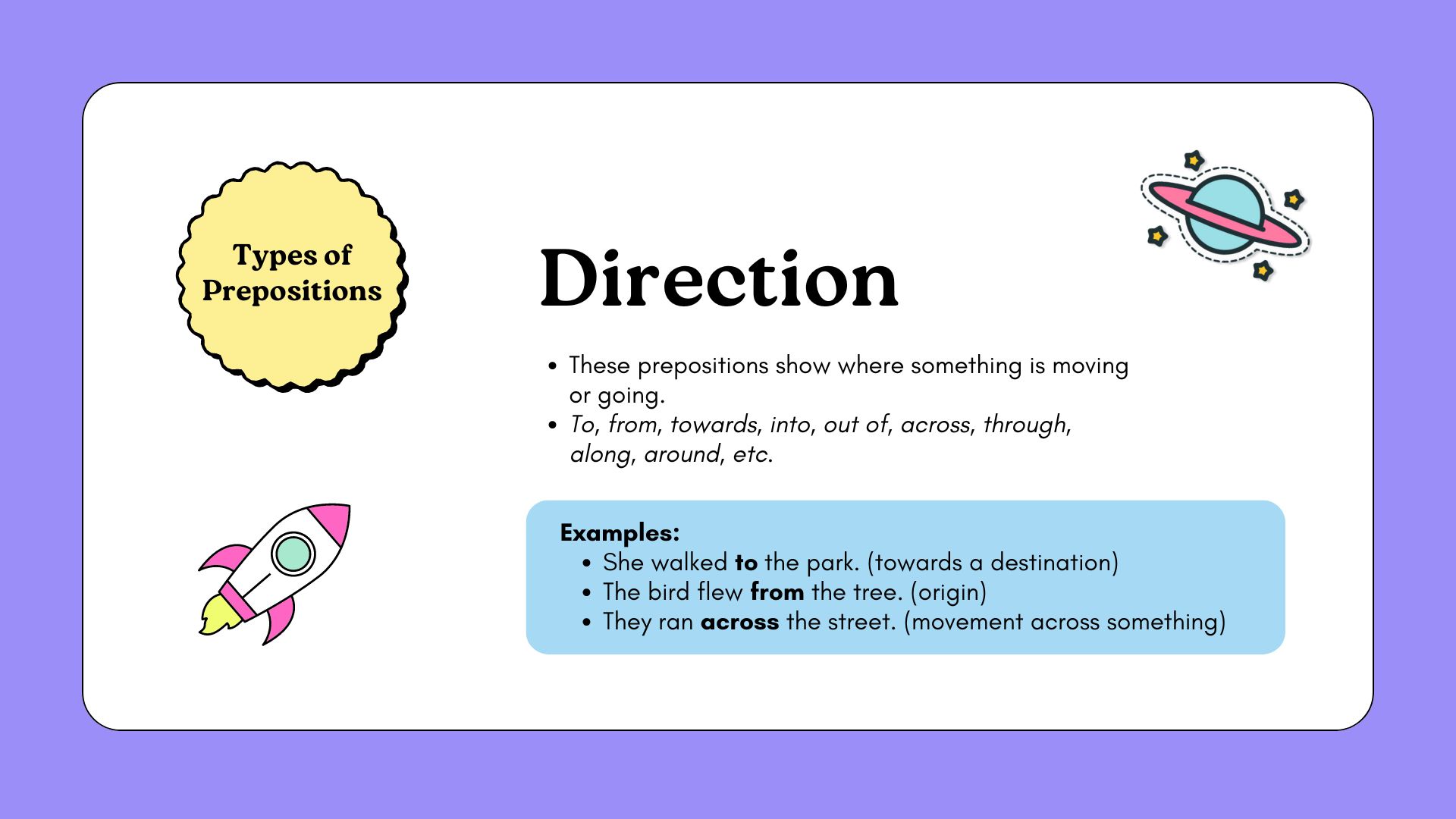
Prepositions of direction are used to indicate the direction in which something moves or faces. Here is a list of common prepositions of direction along with their uses and examples:
- To
- Use: Indicates movement towards a specific place.
- Examples:
- She is going to the store.
- He walked to the park.
- They are traveling to Paris.
- Send this package to my office.
- Towards
- Use: Indicates movement in the direction of something (often without reaching it).
- Examples:
- The dog ran towards the gate.
- She moved towards the door.
- He walked towards the beach.
- The car is heading towards the city.
- Into
- Use: Indicates movement from the outside to the inside of something.
- Examples:
- She walked into the room.
- He dived into the pool.
- The cat jumped into the box.
- Pour the juice into the glass.
- Onto
- Use: Indicates movement from a lower place to a higher place or surface.
- Examples:
- The cat jumped onto the table.
- He climbed onto the roof.
- She stepped onto the platform.
- They loaded the boxes onto the truck.
- Out of
- Use: Indicates movement from the inside to the outside of something.
- Examples:
- She got out of the car.
- He ran out of the house.
- They climbed out of the window.
- The bird flew out of the cage.
- From
- Use: Indicates the starting point of a movement.
- Examples:
- They traveled from New York to Los Angeles.
- The plane departed from London.
- He walked home from school.
- She took a book from the shelf.
- Through
- Use: Indicates movement from one side to the other within something.
- Examples:
- The train goes through the tunnel.
- She walked through the park.
- He looked through the window.
- They drove through the city.
- Across
- Use: Indicates movement from one side to the opposite side.
- Examples:
- She swam across the river.
- He walked across the street.
- They traveled across the country.
- The bridge goes across the lake.
- Over
- Use: Indicates movement above something.
- Examples:
- The plane flew over the mountains.
- She jumped over the fence.
- He looked over the wall.
- The bird soared over the trees.
- Along
- Use: Indicates movement in a line matching the length of something.
- Examples:
- They walked along the beach.
- He jogged along the path.
- The car drove along the road.
- She ran along the river.
- Around
- Use: Indicates movement in a circular direction or around the edge of something.
- Examples:
- They walked around the park.
- He looked around the room.
- The path goes around the lake.
- She turned around the corner.
- Up
- Use: Indicates movement to a higher place or position.
- Examples:
- He climbed up the hill.
- She walked up the stairs.
- The cat jumped up the tree.
- They went up the mountain.
- Down
- Use: Indicates movement to a lower place or position.
- Examples:
- She ran down the hill.
- He walked down the stairs.
- The ball rolled down the slope.
- They went down the mountain.
- Past
- Use: Indicates movement from one side to the other, beyond something.
- Examples:
- She walked past the library.
- He drove past the store.
- They ran past the finish line.
- The parade went past the square.
| Preposition | Use | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| To | Movement towards a specific place | To the store, To the park, To Paris, To my office |
| Towards | Movement in the direction of something | Towards the gate, Towards the door, Towards the beach, Towards the city |
| Into | Movement from outside to inside | Into the room, Into the pool, Into the box, Into the glass |
| Onto | Movement from lower place to higher place | Onto the table, Onto the roof, Onto the platform, Onto the truck |
| Out of | Movement from inside to outside | Out of the car, Out of the house, Out of the window, Out of the cage |
| From | Starting point of a movement | From New York, From London, From school, From the shelf |
| Through | Movement from one side to the other within something | Through the tunnel, Through the park, Through the window, Through the city |
| Across | Movement from one side to the opposite side | Across the river, Across the street, Across the country, Across the lake |
| Over | Movement above something | Over the mountains, Over the fence, Over the wall, Over the trees |
| Along | Movement in a line matching the length of something | Along the beach, Along the path, Along the road, Along the river |
| Around | Movement in a circular direction | Around the park, Around the room, Around the lake, Around the corner |
| Up | Movement to a higher place | Up the hill, Up the stairs, Up the tree, Up the mountain |
| Down | Movement to a lower place | Down the hill, Down the stairs, Down the slope, Down the mountain |
| Past | Movement from one side to the other, beyond something | Past the library, Past the store, Past the finish line, Past the square |
Prepositions of Manner:

Prepositions of manner describe how something is done or the manner in which an action is performed. Here is a list of common prepositions of manner along with their uses and examples:
- With
- Use: Indicates the instrument, object, or feature used to perform an action.
- Examples:
- She cut the paper with scissors.
- He writes with a pen.
- They traveled with a guide.
- She made the cake with love.
- By
- Use: Indicates the method or means of doing something.
- Examples:
- He traveled by train.
- She learned to cook by watching videos.
- They communicated by email.
- The cake was made by hand.
- In
- Use: Indicates a particular state or condition.
- Examples:
- She spoke in a soft voice.
- He completed the task in a hurry.
- They were in good spirits.
- The document is written in English.
- On
- Use: Indicates a specific tool or medium.
- Examples:
- He works on a computer.
- She drew the picture on a canvas.
- The report was prepared on the software.
- They talked on the phone.
- Like
- Use: Indicates similarity or resemblance.
- Examples:
- She sings like an angel.
- He runs like the wind.
- The house is built like a castle.
- They danced like professionals.
- As
- Use: Indicates the role or function of something.
- Examples:
- She works as a teacher.
- He was hired as a consultant.
- They used the room as a storage area.
- She acted as a mediator.
- Without
- Use: Indicates the absence of something.
- Examples:
- He completed the task without any help.
- She spoke without hesitation.
- They traveled without a map.
- He passed the exam without studying.
- In a … manner/way
- Use: Indicates the manner in which an action is performed.
- Examples:
- She handled the situation in a professional manner.
- He completed the project in a timely way.
- They spoke to each other in a friendly manner.
- The work was done in a meticulous way.
| Preposition | Use | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| With | Indicates the instrument or feature | With scissors, With a pen, With a guide, With love |
| By | Indicates the method or means | By train, By watching videos, By email, By hand |
| In | Indicates a state or condition | In a soft voice, In a hurry, In good spirits, In English |
| On | Indicates a specific tool or medium | On a computer, On a canvas, On the software, On the phone |
| Like | Indicates similarity or resemblance | Like an angel, Like the wind, Like a castle, Like professionals |
| As | Indicates the role or function | As a teacher, As a consultant, As a storage area, As a mediator |
| Without | Indicates the absence of something | Without help, Without hesitation, Without a map, Without studying |
| In a … manner/way | Indicates the manner of an action | In a professional manner, In a timely way, In a friendly manner |
Double Prepositions:
Double prepositions are combinations of two simple prepositions used together to express a single relationship. These combinations are used to provide more precise meanings that a single preposition might not fully convey. Here are some common double prepositions, along with their meanings and examples:
- Out of:
- Meaning: From the inside to the outside of something.
- Example: She took the keys out of her bag.
- Up to:
- Meaning: Indicates a limit or an extent.
- Example: The temperature rose up to 40 degrees.
- According to:
- Meaning: As stated by or in agreement with.
- Example: According to the weather forecast, it will rain tomorrow.
- Because of:
- Meaning: Due to; on account of.
- Example: The event was canceled because of the storm.
- Next to:
- Meaning: Beside; in close proximity to.
- Example: She sat next to her friend during the movie.
- Due to:
- Meaning: Because of; caused by.
- Example: The flight was delayed due to bad weather.
- Apart from:
- Meaning: Except for; besides.
- Example: Apart from the initial delay, the trip was enjoyable.
Examples in Sentences
- Out of:
- The cat jumped out of the window.
- He ran out of the building when the alarm went off.
- Up to:
- She can lift weights up to 50 pounds.
- The water level rose up to the edge of the pool.
- According to:
- According to the report, sales have increased this quarter.
- According to her, the project is nearly complete.
- Because of:
- They were late because of the traffic jam.
- He couldn’t attend the meeting because of a family emergency.
- Next to:
- The bakery is next to the coffee shop.
- He always sits next to his best friend in class.
- Due to:
- The concert was postponed due to rain.
- The office is closed today due to a public holiday.
- Apart from:
- Apart from a few minor errors, the document is well-written.
- Apart from her, everyone agreed with the decision.
| Double Preposition | Use | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Out of | Indicates origin or movement away | Shows something leaving or moving out from a place, condition, or state. | “He jumped out of the car.” |
| According to | Refers to source or basis | Indicates following information or guidelines based on a source. | “According to the report, sales are up.” |
| Next to | Shows proximity | Indicates closeness or being beside something. | “She sat next to him.” |
| Because of | Indicates reason or cause | Explains the reason behind an action or situation. | “The game was canceled because of rain.” |
| Up to | Indicates limit or responsibility | Shows an upper limit or responsibility. | “It’s up to you to decide.” |
| In front of | Shows location or position | Indicates a position directly ahead of something. | “The car is parked in front of the house.” |
| In addition to | Indicates inclusion | Adds information or items to what is already mentioned. | “In addition to coffee, they served tea.” |
| By means of | Indicates method or way | Describes the method or tool used to do something. | “She communicated by means of letters.” |
| Along with | Indicates accompaniment | Shows that something or someone accompanies another thing or person. | “He came along with his friend.” |
| Apart from | Indicates exclusion or exception | Shows something excluded or excepted from the main idea. | “Apart from John, everyone agreed.” |
| Ahead of | Shows priority or position | Indicates something in front of or prior to another thing in terms of position or time. | “We arrived ahead of schedule.” |
Compound Prepositions:
Compound prepositions are prepositions that consist of two or more words. These prepositions work together to form a single unit, which functions just like a single-word preposition. They help in expressing more complex relationships in sentences. Here are some common compound prepositions, along with their meanings and examples:
- According to:
- Meaning: As stated by or in agreement with.
- Example: According to the weather report, it will rain tomorrow.
- Along with:
- Meaning: In addition to; together with.
- Example: He came along with his friend.
- Apart from:
- Meaning: Except for; besides.
- Example: Apart from the initial delay, the flight was smooth.
- Because of:
- Meaning: Due to; on account of.
- Example: The event was canceled because of the storm.
- By means of:
- Meaning: Using; with the help of.
- Example: He solved the problem by means of a new algorithm.
- In addition to:
- Meaning: Besides; as well as.
- Example: She is taking Spanish lessons in addition to her French classes.
- In front of:
- Meaning: Before; ahead of.
- Example: The car is parked in front of the house.
- In spite of:
- Meaning: Despite; notwithstanding.
- Example: They went hiking in spite of the bad weather.
- On account of:
- Meaning: Because of.
- Example: The game was postponed on account of the rain.
- With regard to:
- Meaning: Concerning; in relation to.
- Example: With regard to your request, we will need more information.
Examples in Sentences
- According to:
- According to the teacher, the test will be next week.
- According to the instructions, we should mix the ingredients slowly.
- Along with:
- She brought her sister along with her to the party.
- The manager, along with the team, reviewed the project plan.
- Apart from:
- Apart from a few minor mistakes, your report is excellent.
- Apart from her, everyone agreed with the proposal.
- Because of:
- The flight was delayed because of fog.
- She missed the meeting because of a family emergency.
- By means of:
- He fixed the machine by means of a simple tool.
- They communicated by means of sign language.
- In addition to:
- In addition to his salary, he receives a yearly bonus.
- She has to complete her homework in addition to her chores.
- In front of:
- He stood in front of the audience and began to speak.
- The playground is in front of the school.
- In spite of:
- They continued their journey in spite of the heavy rain.
- She achieved success in spite of many obstacles.
- On account of:
- The match was canceled on account of the weather.
- They were late on account of a traffic jam.
- With regard to:
- With regard to your inquiry, we will respond soon.
- With regard to the new policy, there have been mixed reactions.
| Compound Preposition | Use | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Because of | Shows reason or cause | Indicates the reason something happens. | “They were late because of traffic.” |
| In spite of | Shows contrast or concession | Indicates an action happens despite a condition. | “She went for a walk in spite of the rain.” |
| On account of | Indicates reason or cause | Used to show the cause or reason for something. | “The match was postponed on account of the weather.” |
| In front of | Shows location or position | Refers to a position directly before something or someone. | “The statue is in front of the museum.” |
| In addition to | Indicates inclusion | Adds something to what has already been mentioned. | “In addition to coffee, they served pastries.” |
| By means of | Shows method or way | Indicates the method or tool used to do something. | “She travels by means of public transport.” |
| With regard to | Shows reference or relation | Refers to a specific subject or topic. | “With regard to your request, we need more information.” |
| According to | Refers to a source or basis | Indicates information based on a certain source or authority. | “According to the schedule, the meeting starts at 10 AM.” |
| In place of | Indicates substitution | Shows one thing replacing or substituting another. | “She used vinegar in place of lemon juice.” |
| In case of | Indicates condition or contingency | Refers to a situation that might happen and what action to take if it does. | “In case of fire, use the stairs.” |
| Apart from | Shows exception or exclusion | Indicates something excluded from the main idea. | “Apart from Anna, everyone attended the meeting.” |
| In relation to | Shows connection | Refers to something’s connection or relevance to another thing. | “His comments in relation to the policy were insightful.” |
Conclusion:
Prepositions are a fundamental component of the English language, serving as essential connectors that provide clarity, detail, and precision in communication. They indicate relationships between various elements within a sentence, specifying time, place, direction, manner, and more. By mastering the use of prepositions, one can greatly enhance their linguistic abilities, making their speech and writing more coherent and expressive.


